Financial Inclusion In Africa
One of the biggest barriers to Africa’s economic and human growth is still financial inclusion. For instance, just 9.1 million adults (or 14% of adults) in Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda have access to or utilize a commercial bank account.
Access to bank accounts has historically been thought to be a sign of financial inclusion. Banks continue to be essential in enabling access to financial services, even in the face of the spread of fintech innovations and the widespread use of mobile money throughout Africa. Households can save and pay their bills with the use of bank accounts, which also help businesses establish their creditworthiness and get better access to insurance, loans, and other services. As a result, having access to bank accounts is crucial for sustained economic expansion.
The goal of this Zindi competition project is to develop a machine learning model that can identify the people who are most likely to utilize or own a bank account. The models and solutions created can offer insights into some of the major variables influencing people’s financial security as well as an indication of the current status of financial inclusion in Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda.
Becoming One with the Data
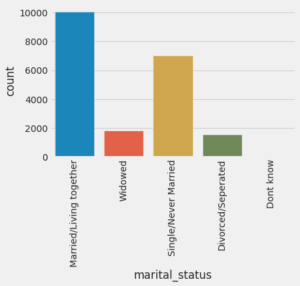
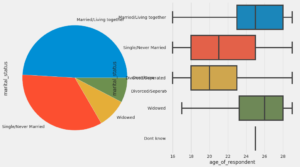
Confusion Matrix
A confusion matrix is a grid showing how often our model confuses different categories. True Positives & Negatives are correct guesses, False Positives & Negatives are mistakes. It helps visualize your model’s strengths & weaknesses in understanding data. The grids will show how confused was our model in experiment :
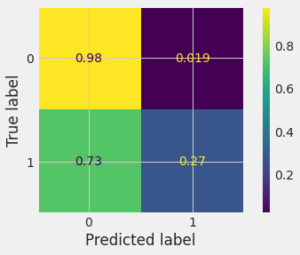
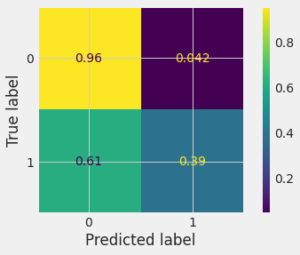
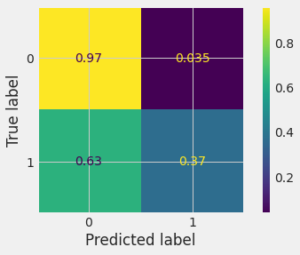
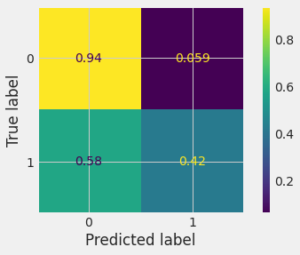
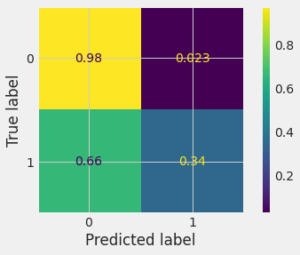
For Code Implementation visit github.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.